We all have medical questions that we want answered – that’s why Dr. Amna Asif is here to provide us with her expert opinion! Every other week, she will be sharing her expert advice with us regarding a range of topics our followers are interested in learning more about. This week in Doc Talk, she talks about rheumatoid arthritis. Read ahead to find out what exactly it is, what the causes and symptoms are, and what you can do to treat it:

What Is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
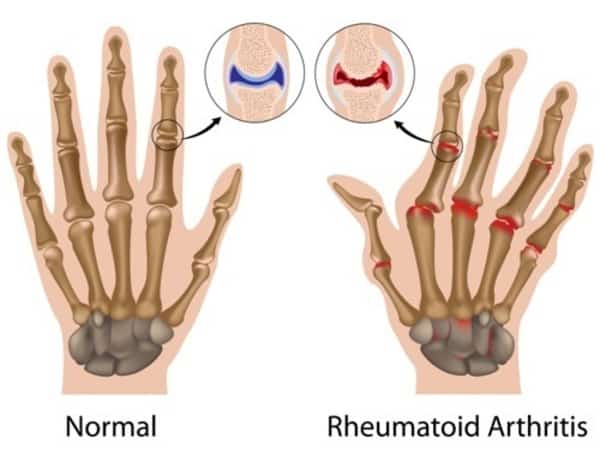
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes pain and swelling in the joints. This happens because the immune system attacks the lining of the joints, causing inflammation and joint damage. RA usually affects the smaller joints, such as those in the hands, feet and wrists, although larger joints such as the hips and knees can also be affected. The ligaments, tendons and muscles surrounding the joint can also be impacted, causing joints to become unstable.
Causes
Rheumatoid arthritis is 3 times more common in women than men. It can occur at any age, but usually appears between individuals 30 to 60 years of age.
The causes of RA are not known but it is more common in smokers and those with a family history of RA. As RA is an autoimmune condition, the antibodies generated in the immune system attack the lining of joints (Synovium) and damage it, leading to inflammation. The chemicals released due to inflammation damage the cartilage, ligaments, tendons and ultimately destroy the joints.
Symptoms
Symptoms of RA vary from person to person. A flare-up of RA is defined as having more intense symptoms and can be intermittent. You may have one or all symptoms.
- Pain and stiffness in affected joints – this is usually worse in the morning
- Redness and warmth at affected sites – due to inflammation joints become hot and tender to touch
- Fatigue
- Fever and sweating
- Dry eyes
- Chest pain, if heart and lungs are involved
Note: If you think you may have the symptoms of RA, it’s important to see your doctor/Rheumatologist. Early diagnosis and correct treatment can reduce the impact of the disease. If left untreated, RA may permanently damage your joints.
Diagnosis
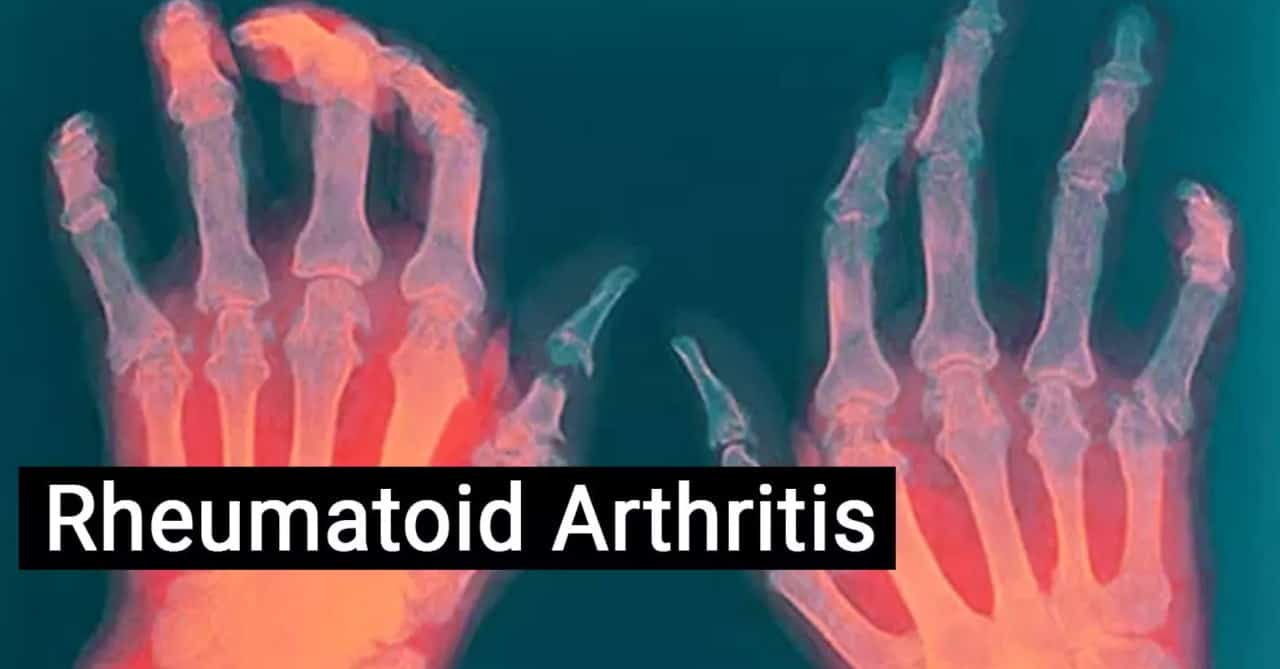
RA can be difficult to diagnose as many conditions can cause joint pain and inflammation. No blood test can definitively diagnose RA, but some blood tests (Like CRP, Rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP test) can suggest that you may have this condition. X-Rays of the affected joints however, can help diagnose different types of arthritis and can reveal how the disease is progressing. Ultrasound and MRI of joints may not be needed but they too can help assess the damage.
How Is RA Managed?
While there is no cure for RA, there are some treatment options which can help improve your symptoms and progression of disease so you can lead a healthy and active life.
The experience of pain is unique to everybody, so what works for you, may not work for someone else. That’s why the treatment is usually tailored to your symptoms, but here are a few options:
- Medicines to relieve your symptoms and help prevent progression of disease
- TENS electrical device
- Physiotherapy and exercises
- Complementary therapies – such as massage, acupuncture, hypnosis and relaxation techniques
- Surgery to correct joint problems
Medicines for RA can be divided into 2 groups:
- Group 1 includes medications which reduce the activity of the immune system that is attacking joints. These medications are termed as “Disease Modifying Anti Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)”. Some of those medications include Methotrexate, Leflunomide, Sulfasalazine, Prednisolone and hydroxychloroquine. There is a newer group of DMARDs called “Biologicals” which help with inflammation. If your are on those medications, you need regular blood test as these medicines may have side effects.
- Group 2 includes medicines which help with symptoms (pain or inflammation), such as Paracetamol, Celecoxib, Ibuprofen etc.
Please consult your Rheumatologist to discuss the treatment option most suitable for you.
Can It Be Prevented?
There is no definite way to prevent RA but there are things you can do to improve your quality of life with RA and ease symptoms. Eating well, staying physically active, stopping smoking and reducing stress can all help.
Complications
Having Rheumatoid Arthritis can increase your risk of developing certain conditions:
- Cardiovascular disease – people with RA have a higher risk of heart attacks and stroke.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome – this is a common condition in people with RA when there is too much pressure on the nerve in the wrist. It can cause aching, numbness and tingling in your thumb, fingers and part of the hand.
- Inflammation of eyes, lungs, heart.
- Vasculitis – Inflammation of blood vessels in different parts of the body
- Tendon rupture around affected joints e.g fingers
- Cervical Myelopathy due to the dislocation of upper spinal joints in the neck
If you think, you may be suffering from Rheumatoid Arthritis, please get in touch with your doctor and get a referral to a Rheumatologist who can start early treatment to prevent permanent damage to your joint.







What do you think?
You must be logged in to post a comment.