Birth control, while an essential part of health care, is often misunderstood. Simply put, contraceptives encompass a range of medicines, devices and methods that aim to prevent pregnancy. This is essential for family planning, allowing women to decide when they want to get pregnant and reducing the chances for an unplanned pregnancy. But that’s not the only use of contraceptives; it also has multiple health benefits including, but not limited to, protection against sexually transmitted diseases, regulating periods, and help with medical problems such as endometriosis or ovarian cysts. It’s important to be informed about birth control but with over 15 different methods of contraceptives, it can be hard to navigate. Here’s a breakdown of your options:

Long-Acting Reversible Contraception
This is sometimes called the “fit and forget” method because you don’t have to worry about the upkeep once they are in place. They are also the most effective method of contraception with a 99% success rate in preventing pregnancies.
- IUDs (aka intrauterine devices) is a small plastic, T-shaped device that is inserted into your uterus to prevent pregnancies and can last from about 3 to 12 years, depending on the type.
- Birth control implants are tiny thin rods – about the size of a matchstick, that are inserted under the skin of your upper arm – releasing the progestin hormone (which prevents ovulation) and lasts for up to 5 years.
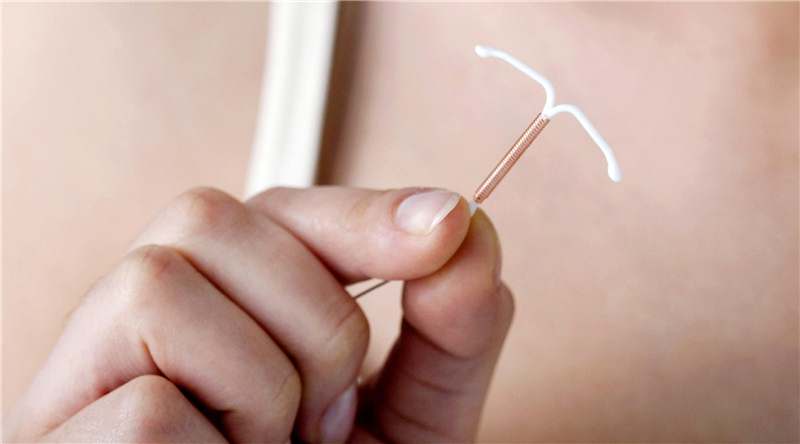
Hormonal Contraceptives
This method uses hormones to prevent pregnancies and has to be used at a regular schedule. They are highly effective methods of birth control, ranging from about a 90 to 95% rate of efficiency.
- Birth control pills are meant to be taken every single day, around the same time each day. Missing multiple doses or taking the pills at odd times can render them less effective or even useless, so make sure you’re keeping track if you choose to go on the pill. There are two types of birth control pills available: combined and progestin-only. Consult your doctor to figure out which one would work best for you. Other than preventing pregnancies, birth control pills also have many health benefits (like preventing acne and regulating your period cycle)!
- Birth control shots are injections that also use the progestin hormone to prevent pregnancies, stop ovulation and make the cervical mucus thicker. Get them regularly every three months for effective contraception.
- Birth control patches are worn on certain parts of the body, which then release hormones through your skin to prevent pregnancies. They have to be replaced weekly to be effective.

Barrier Methods
These are physical devices to stop sperm from entering a woman’s vagina.
- Condoms have been the most popular method of contraception for decades. They are also the only method to protect you from getting or transferring STDs (sexually transmitted diseases), which is why medical experts recommend the use of condoms even if you are on some other form of birth control.
- Internal condoms, aka “female condoms”, are an alternative barrier method. The only difference between these and condoms for men are that the internal condoms go inside the vagina. Besides that, they provide the same protection from pregnancies and STDs as traditional condoms!
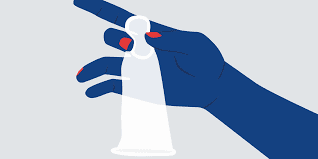
Emergency Contraception
This is a form of contraception to prevent pregnancies after you’ve had unprotected sex, or if your normal method of contraception has failed (like missing more than one contraceptive pill).
- Emergency contraceptive pills, more popularly known as the “morning-after pill”, can be taken up to three days after unprotected sex and are highly effective. It’s the most convenient method of emergency contraception, should you need it.
- Copper IUDs can also be used as emergency contraception, within five days of having unprotected sex, but you will need to contact a doctor to have it inserted.

Permanent Contraception
This is also called sterilisation and consists of procedures that prevent all future pregnancies i.e. vasectomies for men and tubal ligation for women.







What do you think?
You must be logged in to post a comment.